Dermatitis
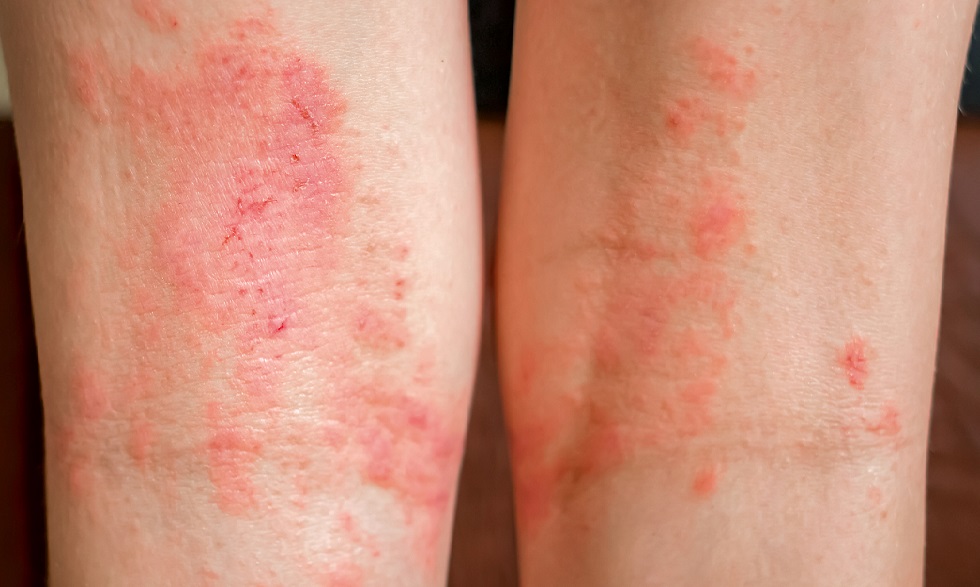
Dermatitis is a general term for skin inflammation. With dermatitis, your skin will typically look dry, swollen, and discolored. The causes of dermatitis vary between types.
However, it’s not contagious. Contact your doctor for an appointment if your skin is infected, painful, or uncomfortable, or if your dermatitis is widespread or isn’t getting better.
Types of dermatitis
There are several different types of dermatitis. Some can last a long time, while others may cycle between flare-ups and periods of no symptoms. Some types of dermatitis are more common in children, and others are more common in adults.
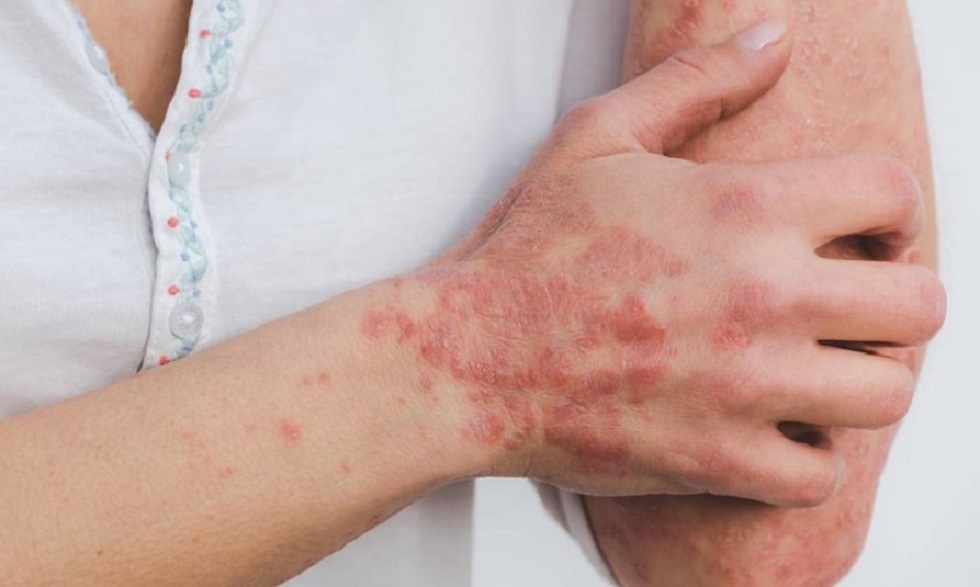
- Atopic dermatitis: People commonly refer to this as eczema. Atopic dermatitis can run in families trusted Source and usually develops during infancy. However, it can also develop in adulthood. There is no cure for atopic dermatitis. People with the condition will typically experience symptoms in cycles of flare-ups, and periods of little to no symptoms. During flare-ups, patches of skin may appear rough, dry, and itchy.
- Contact dermatitis: Contact dermatitis happens when a substance touches your skin and causes an adverse reaction. These reactions can develop into rashes that burn, sting, itch, or blister. Contact dermatitis may be the result of an allergic or an irritant reaction. In irritant contact dermatitis an outside substance directly damages the skin and causes a reaction. Meanwhile, in allergic contact dermatitis, the outside substance may not directly damage the skin but will cause your immune system to react in a way that does so.
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis: In dyshidrotic dermatitis, the skin cannot protect itself. This results in itchy, dry skin, often accompanied by small blisters. It occurs mainly on the feet and hands, and may also occur in people who perspire heavily in these areas.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: People may refer to seborrheic dermatitis as cradle cap when it occurs in infants. This type of dermatitis is most common on the scalp, though it can also occur on the face, chest, and around the ears. It often causes scaly patches, skin discoloration, and dandruff. Stress or lack of sleep can worsen these symptoms.There is no cure for seborrheic dermatitis, but you can treat it effectively.
Related Services

Dr. Priya Diwaker
Dermatologist in Raipur
Dr. Priya Diwaker, completed her MBBS from government medical college, Bilaspur and her post graduation in Dermatology from JJM Medical College, Davangere.
Our other services
Timings
Mon - Sat (09:00Am - 10:00PM) Sun - (10 am–7 pm)
Phone No
+91-74894 92554
address
1st floor, Indian Chilli Square, Shankar Nagar Rd, opposite Vidya Hospital, Geetanjali Colony, Shankar Nagar, Raipur, Chhattisgarh 492001