Intragastric Balloon Placement
for Weight Loss
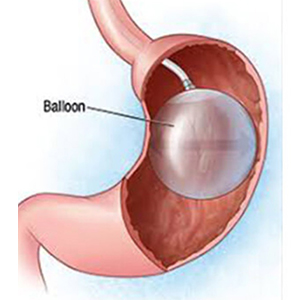
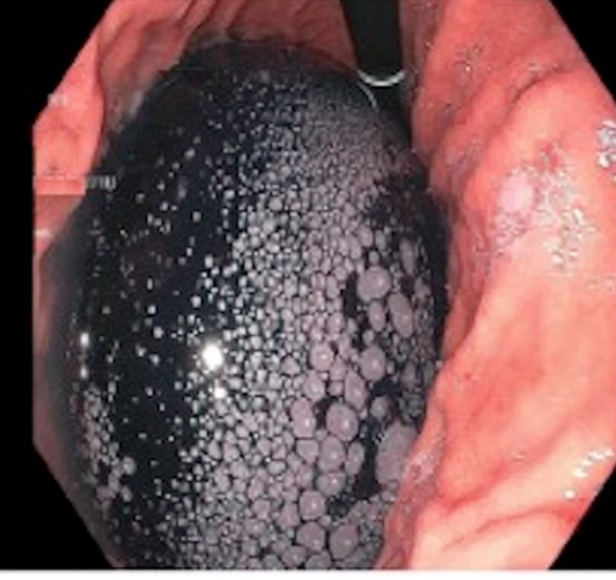
Intragastric balloon (IGB) is a non-surgical method where a deflated balloon is placed in the stomach using endoscopy and then inflated. It helps control appetite and promotes feeling of fullness, aiding weight loss.
Who can get IGB placed?
•Adults (>18 years of age) with BMI of 25-50 kg/m2 who after adequate diet and exercise could not achieve the desirable weight loss.
•Adults with BMI > 40 kg/m2 prior to bariatric or non-bariatric surgery to reduce the surgical risks.
Who cannot get IGB placed?
- Prior surgery involving esophagus, stomach or duodenum.
- Large Hiatus Hernia
- Potential causes of upper GI bleeding
- Achalasia Cardia
- Gastric Mass
- Liver Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension
- Patients unwilling for take medications for the duration of IGB.
How does IGB work in weight loss?
1. Primary Mechanism:
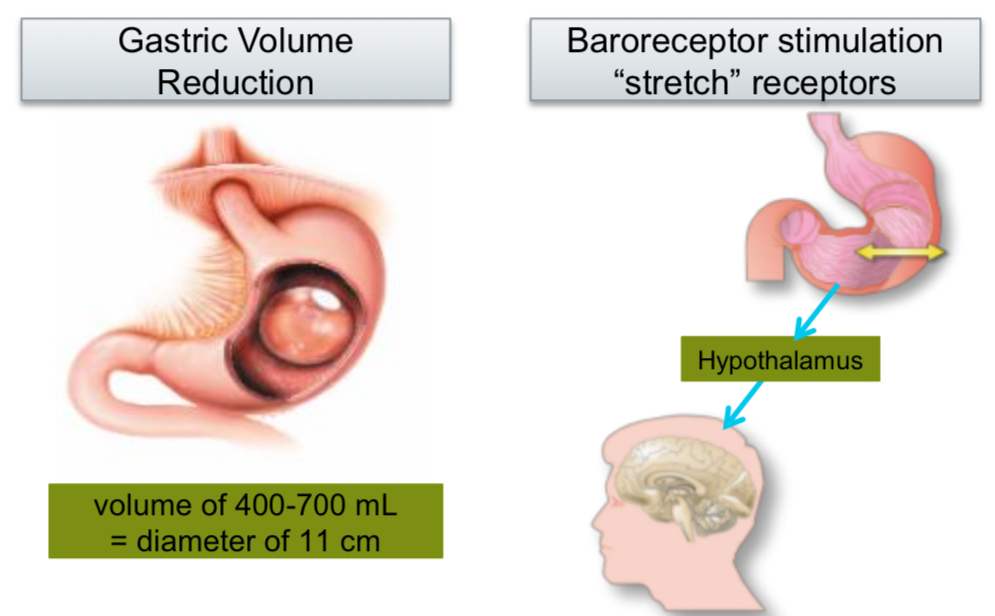
Intragastric balloon decreases gastric emptying
When we eat food, it enters the stomach through the food pipe. In the stomach it stays for some time. During this period digestion occurs and food is moved into the small intestine. Due to the balloon the speed at which the food moves in small intestine is delayed. As a result of this, the individual feels less hungry.
2. Secondary Mechanisms:
- There is reduction in gastric volume and thus reduces the amount of food consumed.
- Due to the balloon, there is stretch in the stomach, that sends negative signal for hunger to the brain.
How is IGB placed?
Placement of IGB is carried out in an Endoscopy Suite. Intravenous conscious sedation is administered and the throat is sprayed with local anesthetic. Endoscopic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract is performed. The endoscope is then withdrawn. The IGB in its collapsed state is introduced into the stomach via the mouth. Once in the correct position the IGB is inflated with air and the introducer tube is detached and removed.The entire procedure takes about 15 minutes.Patients are carefully monitored during the endoscopic procedur and during a short recovery period until they are alert. Very rarely in some situations of emergency, patients may require urgent hospitalization and need shifting to nearby hospital.
What are complications related to IGB?
There are rarely any complications with the use of the IGB. During endoscopy and the placement or removal of the IGB
- Injury to the throat, esophagus or stomach, causing bleeding or even perforation may occur requiring surgical repair.
- While the IGB is in place: Gastric ulcers or erosions may be caused by the pressure on gastric mucosa.
- Obstruction of the gastro‐intestinal tract may result if a balloon leaks and moves from its correct position. Surgical removal of the balloon may then be necessary.
- Adverse reactions to the presence of the IGB:
Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, reflux, bloating and cramps may occur. These symptoms are often temporary and can usually be treated with medications.In the rare cases where vomiting does not subside, the IGB may have to be removed. If the IGB causes intolerable or untreatable sideeffects it can be removed at any time.
What are the precautions after IGB placement?
Few patients may feel nausea and vomiting for few days. They may feel abdominal fullness. Most of symptoms can be managed with medications. Patient has to be on one medication of acid suppression for entire duration of intragastric balloon.
